Advanced Git
Git Rebase
What is git rebase?
As mentioned in a previous post, Git is used for version control. In essence, it is a journal for you code. With Git you can choose to write code starting from a certain part in it’s history and create what is called a branch. You can then merge your branch into the original code. Rebasing is the process of combining those commits to a new base commit. Instead of having a branch off of where you branched off, when rebased, the code of the branch ond original code now have the same base.
What are some advantages and disadvantages of git rebase?
Advantages:
- Git rebase makes the history of your code linear.
- Makes debugging easier since there is a clean history.
Disadvantages:
- Git rebase can change the history of commits and make it harder to see the true past versions of files
- Git rebase makes it more difficult to solve conflicts since they must all be solved individually.
When shouldn’t you use git rebase?
You should not use git rebase on commits that exist outside of the repository on which you are working. This would cause collaborators a lot grief if they are working on another commit, they would have to re-merge their work and re-pull.
Examples:
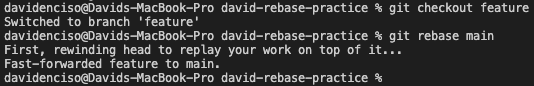
A rebase merge
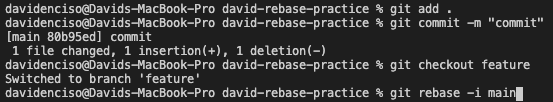
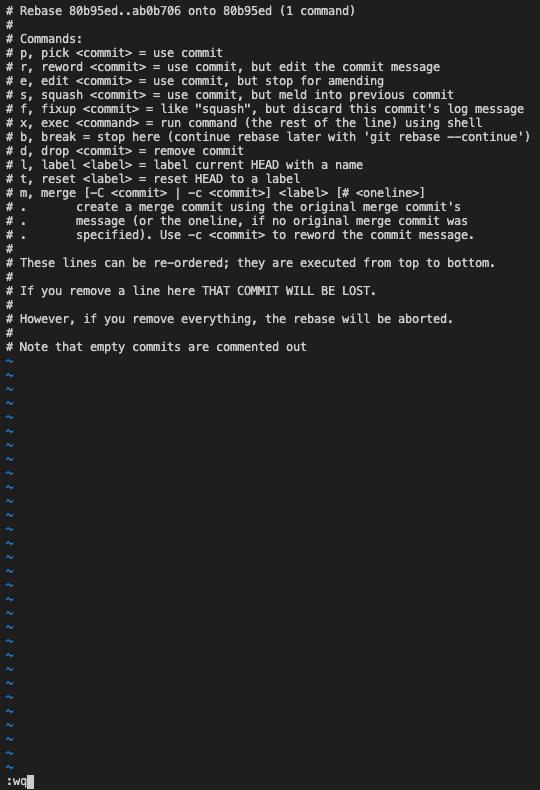
An interactive rebase merge

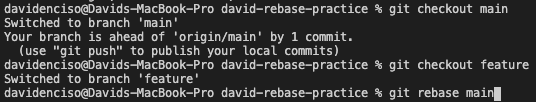
When you shouldn’t rebase with a remote repo
Git Reset, Checkout, and Revert
What is git reset?
Git reset is a pretty strong command to use. Essentially, it undoes the local changes of the state of the repo. There are different kinds of reset that you can do and they are listed below:
Hard
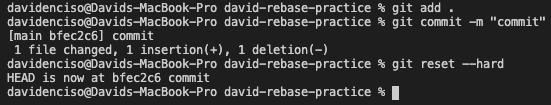
By adding --HARD to the end of git reset you are reseting the working directory, the staged snapshot of your code, and the commit history.
Mixed
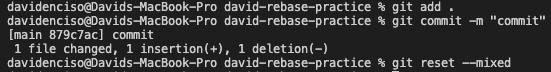
By adding --MIXED to the end of git reset you are reseting the staged snapshot of your code and the commit history.
Soft
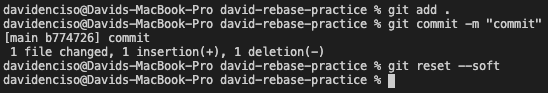
By adding --SOFT to the end of git reset you are just changing the commit history.
What is git checkout?
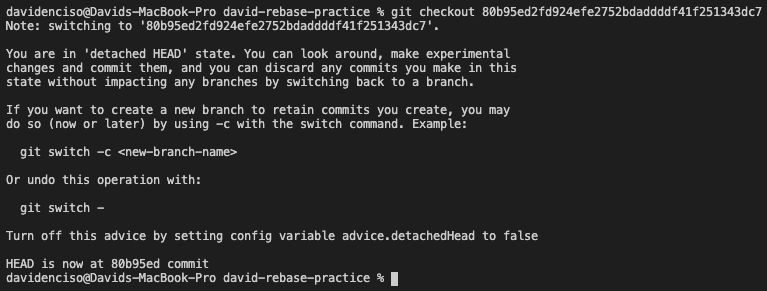
Git checkout is a command that allows you to navigate between branches. In addition, if you write the command git checkout -b "name" you can create and navigate to a new branch at the same time.
What is git revert?
Git revert is nice because instead of simply undoing, deleting, and orphaning commits, it makes a new commit that changes the code to a previous commits. This makes it easier to track the history of that code.
In what ways are these commands the same and what ways are they different?
Git revert and git reset are similare in that they both change the state of your code. The difference is that revert does it in a way that you can still track the history of your code. Reset, on the other hand, erases that history and orphans those commits which will eventually be cleaned out and lost forever.
When would you use reset, checkout, or revert?
You would use reset when you realize you have made some bad commits that you would like to undo and no longer keep track of. You could use checkout when you would like to branch off of your current code and make a new branch that you can make new changes on but also keep the original on the main branch. you would use revert when you would like to undo changes you make to the commit history, but track that history at the same time.
Examples:
Git reset
Hard
Mixed
Soft
Git checkout
Commit
File

Git Revert
Git Submodules
What are git submodules?
Git submodules are repositories inside of other repositories. They don’t seem to be too common but who knows, you might run into one some day. In order to clone a repository and its submodules, you must add --recurse-submodules to the end of your git clone command.
When would you use a submodule?
You would use a submodule in order to keep the commits of your project separate from the repository you are cloning into your project.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of git submodules?
The advantages to having submodules in your repository are that you can work on different part of the project and have commits dedicated only to that submodule. The disadvantages are that it does add quite a bit of complexity to your repository which in turn makes it harder to use for those with whom you are collaborating.